Are you standing in the paint aisle, overwhelmed by the endless choices and unsure what…
What is graphene technology?
What is graphene:
This technology is nothing short of a scientific wonder. First discovered in 2004 by Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov, the uses that have been found for it are almost endless.
It is the finest, lightest and strongest material known to man. Alongside its flexibility and strength, it is also the best-known conductor of heat and electricity. Two of the main reasons for its electrical conductivity are the fact that the material has no band gap and an electrochemically active surface area.
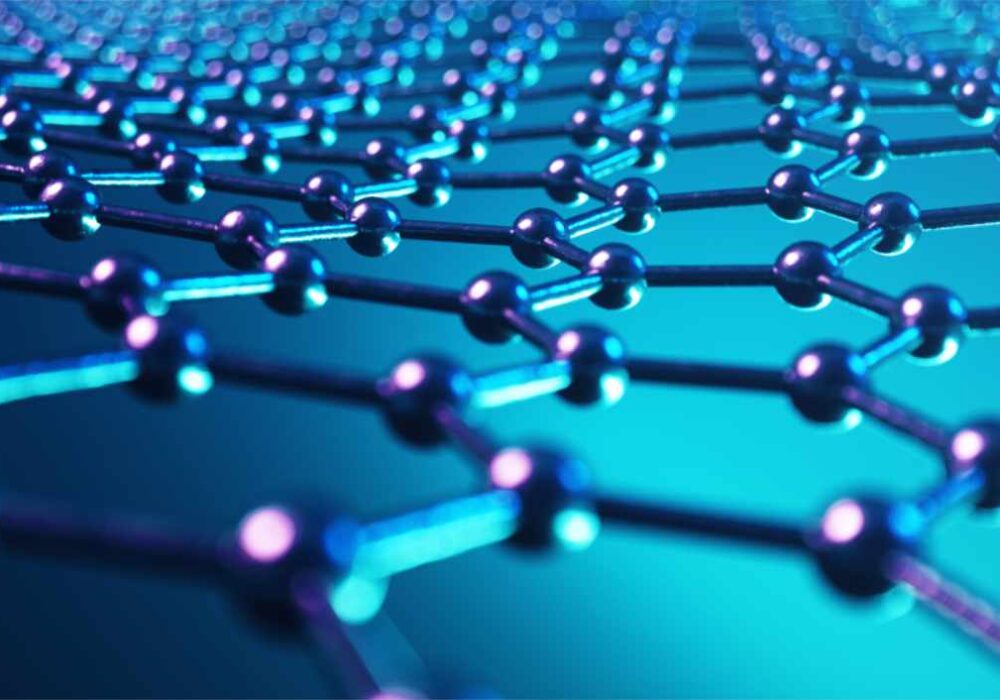
So, what exactly it is? It’s a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a way that represents a honeycomb. To give you an idea of its size, if you were to stack three million layers on top of each other, it would only just be visible as a small graphite crystal.
Here is everything you need to know about this technologies and the way that this fascinating material is being used to change the world.
How does graphene work?
Graphene is a two-dimensional material. Considering most things are three-dimensional, this is a rare occurrence. Because it is 2D, this affects the way the material works. For example, electricity flows through it at a much faster rate with almost no resistance, meaning Graphene has the best electrical conductivity of any material in the world.
It also has no band gap. A band gap is a range of energy in a solid where electrons can’t exist. This lack of a band gap makes more of a metal than a material. This low band gap, mixed with the material’s active surface area, is another contributing factor to graphene’s conductivity. Scientists at Advanced Light Source (ALS) are still analysing ways to create a band gap in graphene applications to see what other uses can be found for the material. With a band gap in place, who knows what other technologies will be created with this?
It is also one of the strongest materials in the world. This is because its arrangement of carbon atoms is joined by a covalent bond. This is a bond that is formed between atoms when they share electrons so that they can have a full outer shell. Under a microscope, graphene looks like hexagons attached to one another. In reality, this is carbon atoms attached to carbon atoms, which is the strongest bond known to science.
This is the opposite of graphene oxide, which is carbon mixed with oxygen. It is an oxidized form of graphene. Although oxide isn’t used in as many industries, it still has multiple benefits, including being used in cancer treatment. Both aren’t just revolutionising science, they’re saving lives.
What is so special about graphene?
What is so special about Graphene is how many uses it has. Usually, something super strong and durable isn’t flexible, but it is the world’s strongest material, and it’s so adaptable that it is used in products that need flexibility, like paints and fabrics.
It is also the most conductive material in the world, conducting 1000 X more electricity than copper. Alongside being a great conductor of electricity, graphene is also an excellent conductor of heat, and is an even better heat conductor than diamond, only becoming damaged by heat after an absolute high temperature of over 800c.
This conductivity is due to graphene having no band gap. It is currently the only known material with zero band gap. Until graphene was discovered, it was thought that only metals had zero band gap.
However, what is so amazing about it, is how simply it was found. Graphene is just a very small piece of graphite, which can be found in the tip of a pencil. In 2004 two Russian scientists, Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov, took a piece of graphite and stuck scotch tape to it. They then began to peel layers of scotch tape off to see what was left on the tape once it had been removed from the graphite. The answer was Graphene.
A scientific breakthrough that scored both Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov a Nobel Prize in physics was found in the same material that people had been using to write with for years, and no one realised that it had more uses than jotting down notes!
What is graphene used for and why?

When graphene was first discovered by Andre Geim, he and his partner had no idea just how useful it would turn out to be. It is now primarily used in the energy industry, being applied to everything from batteries to nuclear power plants. In 2017, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) researchers found that Graphene can be applied to solar cells. What impressed the researchers was the idea that graphene could be used in solar cells and installed on any surface due to its flexibility and transparency. These cells could be applied to the roof of a building or used to cover a car.
Other than its use in solar cells, another one of Graphene’s revolutionary traits is its ability to purify water. Scientists from Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) invented Graphair. Graphair is a soybean-based version of graphene which is used as a highly effective water filter. It’s cost-effective and environmentally friendly, which means it has the potential to change the world and saves lives.
A third use for graphene technologies is in ink. University Cambridge produces graphene ink. Graphene ink is eco-friendly, non-toxic, and suitable for a variety of different printing methods.
Alongside its use in solar cells and ink, there are also graphene fabrics available on the market. Graphene fabrics make up a multitude of men’s and women’s wear. For example, you can get graphene fabric winter coats and even graphene fabric jeans. What is so surprising about graphene fabric is how cost-effective it is. You’d think that such a useful material would have a high price tag!
When oxidised, it becomes graphene oxide, which is currently being used in medicine to activate immune cells and treat illnesses. Graphene is changing technology, and graphene oxide is changing lives.
Is graphene a smart material?

A smart material is a material that changes when it’s exposed to an external stimulus. For example, you could have an umbrella that automatically opens when it detects water and closes when it stops raining. One day smart materials could be used to create technology that automatically repairs itself and could also be used in the human body to fight disease.
When you think of advanced materials, It is the first that springs to mind. Many of its properties, including its high conductivity and durability, make it suitable to be a smart material. It is already being used in some industries for this purpose and studies are continually taking place to explore how else it can be used. Existing examples as a smart material are graphene-asphalt and graphene-concrete composites.
These are being tested as low-carbon alternatives to roads and pavements. They’re more durable than their concrete counterparts and are being tested as road condition sensors. Road condition sensors are sensors that pick up on weather conditions and relay the information to the relevant parties. For example, if there is snow and ice on the road, then the condition sensors will pick this up and create an alert that says there isn’t much grip on the road.
You might be wondering how scientists plan to get so many different applications when creating it takes so much time. After all, it is just a collection of carbon atoms. The answer is through chemical vapour.
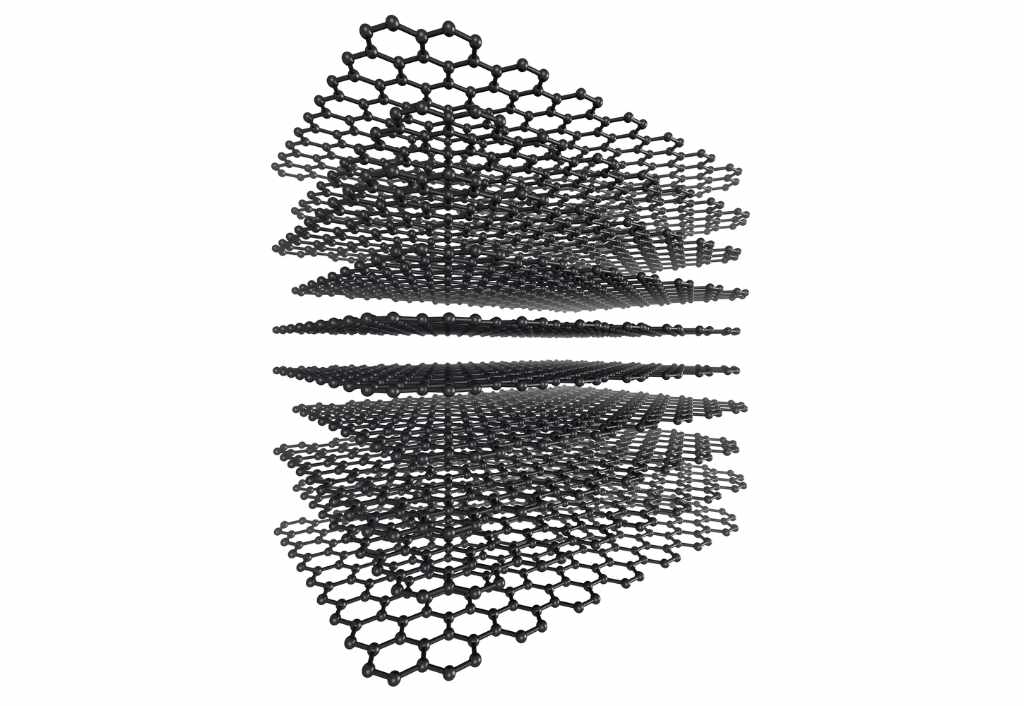
Chemical vapour is a collection of gas molecules combined in a reaction chamber. Using this process, scientists can join the required amount of carbon atoms together, creating layers. These graphene layers can then be combined to create larger quantities of graphene.
The creation of these layers is crucial to the materials’ success as a smart material. The more layers are created, the more graphene can be provided to the different sectors that need it, like solar power and medicine.
What are the benefits of Graphenstone’s graphene technology in our paint?

Andre Geim’s discovery has revolutionised many industries, including ours. By implementing these technologies into our products, we have created a range of long-lasting paints. They’re durable and resistant to water. They won’t crack or peel, and come in every colour and shade you can imagine.
Graphene technology – find out more
Save time, effort and energy today by browsing our full range of graphene-enhanced paint here.







This Post Has 0 Comments